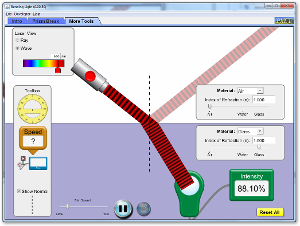
Task 1a: When we carried out the investigation we measured the angles of incident and reflection. Your diagram should look
something like this.

The normal is an imaginary line which extends at right angles from the surface where a wave hits a surface.
Task 1b Refraction is the bending of light as a light ray passes from one medium to another.
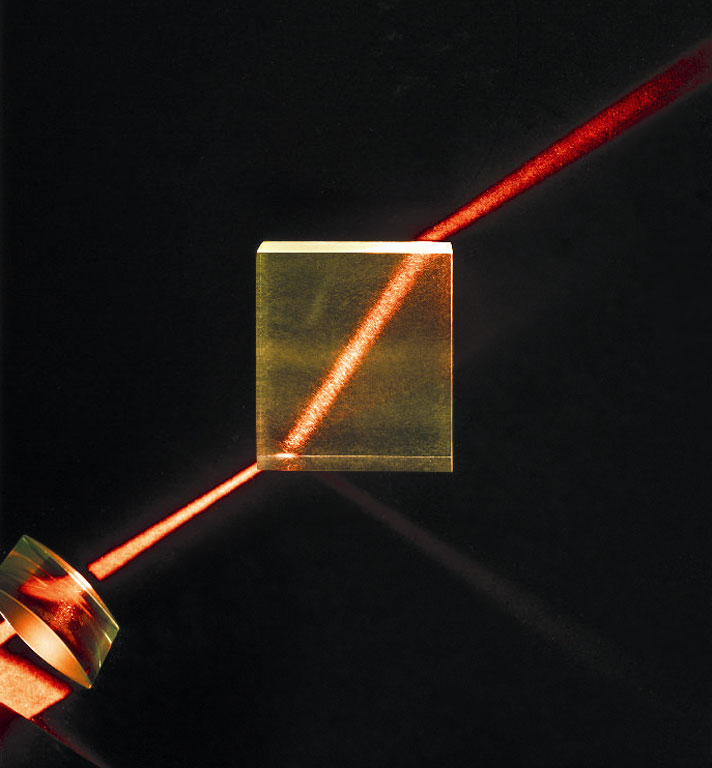
This is caused by the fact that waves travel at different speeds in different media. You should have a diagram of the various angles that you tested and should find that....
when light goes from a less dense to a more dense medium light is refracted towards the normal.
Bitesize info on refraction
The simulation below can be used to not only test different materials but also to establish what is known as the critical angle for a substance which is what you need to do for the next task.
Task 1c: Normally, when a wave hits a new media some of the wave is reflected and some passes through (it is refracted). However, beyond a certain point (known as the critical angle) all of the light is reflected. This is dependent on the two materials. You will need to download the simulation (on a home computer) and establish (and record in a table) the critical angles for a range of different materials. Make sure you draw a diagram and state that the Phet simulations were used for this exercise.
Task 2:
This task looks to combine everything you have learned so far regarding reflection and refraction onto a poster showing how they can be used. You will need an explaination and diagrams of the mirrirs and glass block you have used in the experiments as well as an explanation of these processes.
As part of this you will need to show some examples Plain wing mirrors and
convex rear view mirrors in cars using reflection.
Fiber optic cables in an endoscope using refraction.
Convex mirroed telescopes thast use both.
Task 3: You will need to carry out the research tasks yourselves but I ca help with the diagram of soundwave. The rest though you will need to find yourself.
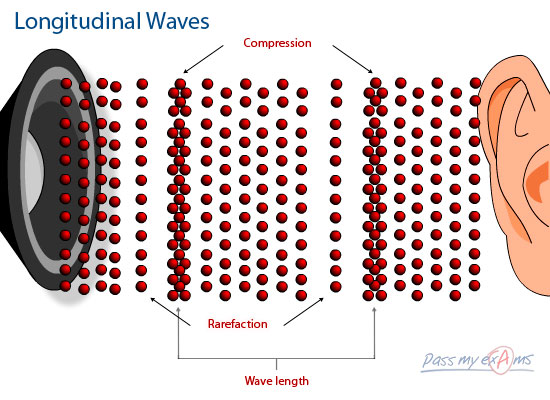 and also some basic information:
and also some basic information:
Human hearing is between 20Hz and 20,000Hz.
Speed of sound 330m/s in air
in water = 1500m/s
in brick = 3000m/s
in iron = 5000m/s
Ultrasound imaging
An image is generated by listening to a series of echos from a single emitted sound. This is due to the fact that when a soundwave hits a different material some of the sound will pass through and some of it will be reflected. This means that if you know how fast a wave should be travelling through a material (such as bone or muscle) then you can build an image.